
Ancestral character state estimation with Arbor
collection: traitAncestralStateEstimation
Ancestral state estimate uses some model of evolution - for example, Brownian motion or an Mk model - and estimates ancestral character states for each node in a phylogenetic tree. For example, if we were interested in the evolution of limb presence or absence among squamates (snakes and lizards), we could use ancestral state estimation. We would use a tree and character data from living species to reconstruct character states (limbs or not) for each internal node in the tree.
It can be difficult to estimate ancestral character states, so most methods return estimates along with some measure of uncertainty. For example, an ancestral state estimate for limbs in squamates might return an estimate with 80% of the marginal likelihood for a limbless state, and 20% for a limbed state - in other words, we think that this species did not have limbs but we are not sure based only on the tree, data, and model of evolution.
Estimating ancestral character states requires three things:
- a phylogenetic tree with branch lengths
- data for the tips of the tree. In Arbor, you don’t have to have a perfect match between the species in the tree and in your data file - but anything that is missing from either of those will be dropped from the analysis.
- a model of evolution
How to do this analysis in Arbor
Arbor provides several ways to estimate ancestral character states. The easiest option is to use the Arbor App Ancestral state estimation.
You can also estimate ancestral character states in Arbor Workflows using the aceArbor function.
More details: aceArbor (Arbor Workflows function)
aceArbor is a function for carrying out ancestral state reconstruction. It works for both discrete and continuous variables, and can reconstruct ancestral character states under both a maximum-likelihood and a Bayesian framework. The function returns results in two formats: a table of ancestral state estimates for each node in the tree, and a plot of the results.
aceArbor assumptions
- known phylogenetic tree with branch lengths
- specified model of evolution (see below)
- tip character states known without error
aceArbor inputs
- table: A data table including species names
- tree: A phylogenetic tree
- column: The name of the column to analyze
- type: The character type
- discrete: a character with a discrete number of states
- continuous: a continuously varying character
- fromData: will attempt to determine the data type from the data itself
- method: specifies the method used to reconstruct ancestral character states
- marginal: marginal ancestral state reconstructions, which reconstruct each node integrating over all possibilities at all other nodes in the tree; this is typically the method used in the literature to reconstruce ACEs
- joint: joint ancestral reconstructions, which give the configuration of ancestral states that together maximize the likelihood of the data given model parameters
- mcmc: reconstruct ancestral states using Bayesian MCMC. Note that the discrete version of this doesn’t seem to work, and even if it did work it is not a full MCMC ancestral state method
- stochastic: create stochastic character map
aceArbor outputs
- a table and a plot with results of the ancestral state reconstruction.
aceArbor example
From the docs page, get anolis.phy and anolis.csv. Load these files into Arbor, and use them as inputs to the aceArbor function. Choose the “ecomorph” column for analysis, and select type: discrete and method: marginal.
Your results should look like this.
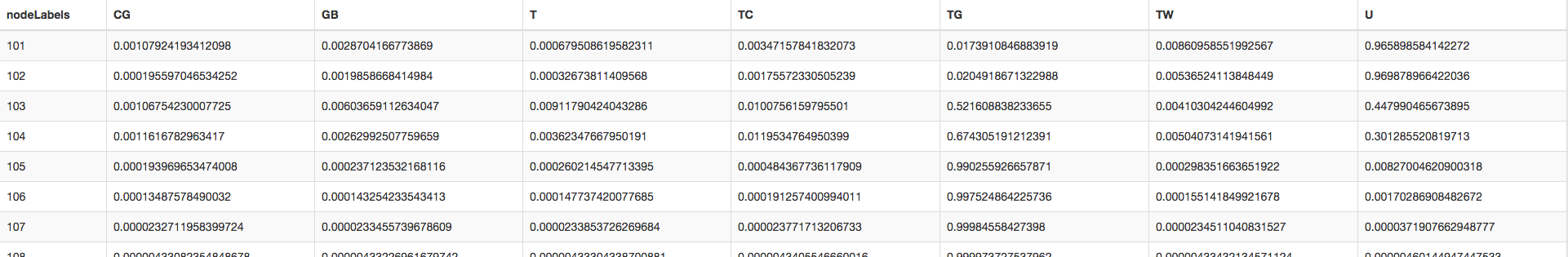
Table: A table showing the internal nodes of the tree (numbered following ape’s scheme) along with marginal likelihoods for each character state.
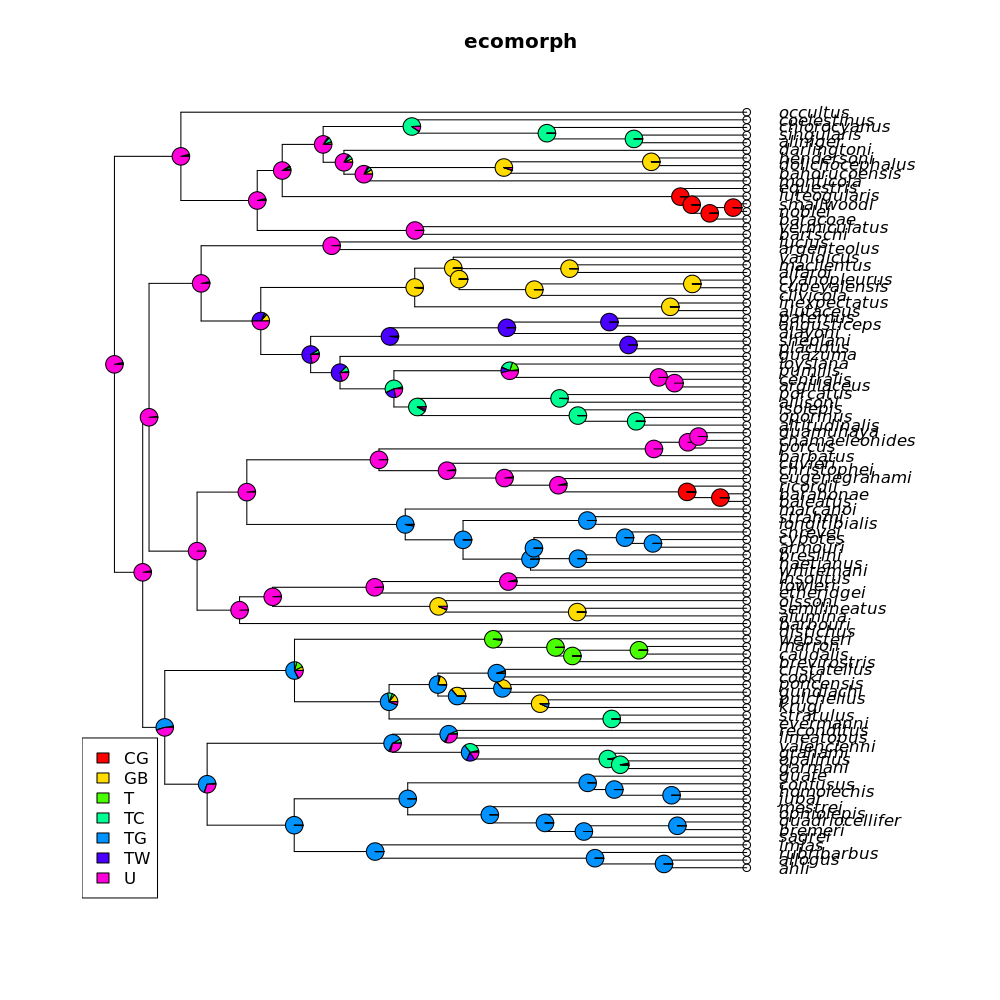
Plot: A plot of the tree with ancestral state estimates at every node.
aceArbor example of use in a workflow
You can see a tutorial for constructing a workflow that involves aceArbor here.
aceArbor citations
Lewis, P.O. 2001. A likelihood approach to estimating phylogeny from discrete morphological character data. Systematic Biology 50:913-925.
Pagel, M. 1999. The maximum likelihood approach to reconstructing ancestral character states of discrete characters on phylogenies. Systematic Biology. 48: 612-622.
Schluter, D., T. Price, A. O. Mooers, and D. Ludwig. 1997. Likelihood of ancestor states in adaptive radiation. Evolution 51: 1699.